Java 직렬화 (Serialization)와 역 직렬화 (Deserialization) 란
Java 객체의 직렬화(Serialization)와 역 직렬화(Deserialization)의 개념과 사용 예시에 대해 알아봅니다.

개요
이 포스팅에서는 Java 객체의 직렬화(Serialization)와 직렬화된 정보를 Java 객체로 만드는 역 직렬화(Deserialization)에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
자바 직렬화, 역 직렬화란?
우리는 살면서 중요한 정보를 잊지 않기 위해 메모를 합니다. 이처럼 자바의 객체를 비휘발성 메모리에 저장했다가 꺼내 쓸 수 있고, 프로그램을 재시작한 후에도 저장된 객체 정보를 불러올 수 있다면 어떨까요? 이를 가능하게 하는 것이 직렬화, 역 직렬화입니다.
자바 직렬화는 객체를 스트림을 통해 연속적(serial)인 데이터로 변환하고, 다시 데이터를 객체로 역 직렬화 할 수 있습니다. 직렬화를 활용하면 단순히 객체를 저장 및 복원하는 것이 아니라, 다양한 자바 서비스 간 객체 정보를 유기적으로 공유할 수도 있습니다.
자바 직렬화 사용방법
자바의 직렬화는 ObjectOutputStream.writeObject(Object o) 메소드를 사용하여 객체를 직렬화할 수 있으며,
직렬화 대상 객체는 직렬화 가능한 클래스의 인스턴스여야 합니다.
이러한 직렬화 가능한 클래스가 되는 방법은 두 가지가 있습니다.
Serializable인터페이스를 구현(implements)한다.- 직렬화 가능한 클래스를 상속한다.
Serializable 인터페이스
Serializable 인터페이스는 구현해야 하는 메소드가 없는, 객체 직렬화를 명시하는 용도의 마크 인터페이스입니다.
다음은 Serializable 인터페이스를 통해 어떤 식으로 직렬화를 수행하는지 알아보겠습니다.
public class ObjectOutputStream extends OutputStream implements ObjectOutput, ObjectStreamConstants {
// ...
private void writeObject0(Object obj, boolean unshared) throws IOException {
// ...
if (obj instanceof String) {
writeString((String) obj, unshared);
} else if (cl.isArray()) {
writeArray(obj, desc, unshared);
} else if (obj instanceof Enum) {
writeEnum((Enum<?>) obj, desc, unshared);
} else if (obj instanceof Serializable) {
writeOrdinaryObject(obj, desc, unshared);
} else {
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
throw new NotSerializableException(cl.getName() + "\n" + debugInfoStack.toString());
} else {
throw new NotSerializableException(cl.getName());
}
}
// ...
}
}ObjectOutputStream 클래스의 private 메소드인 writeObject0() 내부에서 String, Array, Enum, Serializable 이외의
객체의 경우에는 NotSerializableException 예외를 던지는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
다시 자바 직렬화 사용방법으로 돌아와서, 직렬화를 통해 객체를 byte로 변환하는 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
public class User implements Serializable {
private final String name;
private final int age;
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
User user = new User("Dave", 30);
/* 직렬화 */
byte[] bytes = serialize(user);
}
/* 직렬화 메소드 */
public static byte[] serialize(Object o) throws IOException {
try (ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
try (ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos)) {
oos.writeObject(o);
return baos.toByteArray();
}
}
}
}-
직렬화 가능한 클래스 :
User객체를 직렬화 가능한 클래스로 만들기 위해Serializable인터페이스를 구현했습니다. -
직렬화 :
객체 직렬화는ObjectOutputStream클래스의writeObject()메소드를 통해 직렬화할 객체를 전달하고,ByteArrayOutputStream클래스의toByteArray()메소드를 통해 객체를 직렬화한 byte 값을 얻습니다.
어디까지 직렬화가 될까?
자바의 직렬화를 하는 방법에 대해서 간단하게 알아보았습니다. 그렇다면 자바의 직렬화는 어디까지 가능할까요?
다음 몇 가지 예시를 통해서 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
- 부모 클래스에
Serializable구현 - 자식 클래스에
Serializable구현 - 직렬화 가능한 클래스가 직렬화 불가능한 객체를 맴버 변수로 참조
위 각각의 경우에 대해 직렬화 범위에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
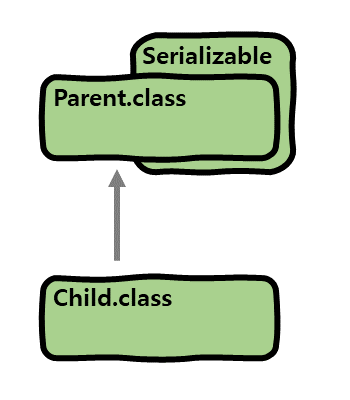
부모 클래스에 Serializable 구현
부모 클래스가 Serializable을 구현하여, 직렬화 가능한 클래스일 때 부모 클래스와 자식 클래스의 직렬화 가능성에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
public class Parent implements Serializable {
private final String name;
public Parent(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}public class Child extends Parent {
public Child(String name) {
super(name);
}
}Parent: 부모 클래스인Parent는Serializable을 구현하였기 때문에 직렬화가 가능합니다.Child: 자식 클래스인Child는 직렬화 가능한 클래스인Parent클래스를 상속하였기 때문에 직렬화가 가능합니다.
자식 클래스에 Serializable 구현
부모 클래스는 직렬화 가능한 클래스가 아니며, 자식 클래스는 Serializable을 구현하여 직렬화 가능한 클래스일 때
부모 클래스와 자식 클래스의 직렬화 가능성에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
public class Parent {
private final String name;
public Parent(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}public class Child extends Parent implements Serializable {
public Child(String name) {
super(name);
}
}Parent: 부모 클래스인Parent는 직렬화 가능한 클래스가 아니므로 직렬화가 불가능합니다.Child: 자식 클래스인Child는Serializable을 구현하였기 때문에 직렬화가 가능합니다.
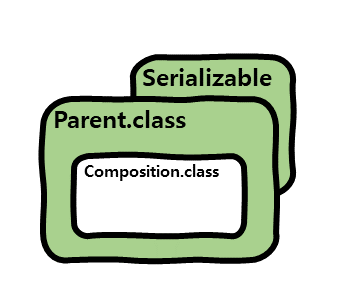
직렬화 가능한 클래스가 직렬화 불가능한 객체를 맴버 변수로 참조
직렬화 가능한 클래스가 직렬화 불가능한 객체를 맴버 변수로 참조하는 경우 해당 클래스의 직렬화 가능성에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
public class Parent implements Serializable {
private final String name;
private final Composition composition;
public Parent(String name, Composition composition) {
this.name = name;
this.composition = composition;
}
}public class Composition {
private final String name;
public Composition(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}위 경우에는 Parent 클래스가 직렬화 가능한 클래스이지만, 직렬화 불가능한 객체인 Composition을 맴버 변수로 참조하여
직렬화 시, NotSerializableException 예외가 발생합니다.
이를 해결하기 위해서는 두 가지 방법이 있습니다.
Composition클래스를 직렬화 가능한 클래스로 만든다.Parent클래스에서 직렬화 불가능한 객체의 맴버 변수composition에transient를 붙여,composition을 직렬화 대상에서 명시적으로 제외한다.
다음은 transient을 사용한 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
public class Parent implements Serializable {
private final String name;
private final transient Composition composition;
public Parent(String name, Composition composition) {
this.name = name;
this.composition = composition;
}
}public class Composition {
private final String name;
public Composition(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}위와 같이 Parent 클래스 내부의 composition 맴버 변수에 transient를 붙이게 되면, Parent 객체를 직렬화 할 때,
composition을 제외하고 직렬화를 수행하여 NotSerializableException 예외가 발생하지 않습니다.
지금까지 자바의 직렬화에 대해 알아보았습니다.
다음으로는 역 직렬화에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
자바 역 직렬화 사용방법
자바의 역 직렬화는 ObjectInputStream.readObject() 메소드를 사용하여 데이터를 객체로 역 직렬화할 수 있으며,
자바 객체를 직렬화하여 얻은 데이터를 가지고 다시 클래스로 만드는 역 직렬화를 할 수 있으며, 다음 두 가지 조건을 만족해야 합니다.
- 직렬화된 객체의 클래스가 Class Path에 존재해야 한다.
- 직렬화된 객체의 클래스가 import된 상태여야 한다.
다음은 직렬화로 얻은 byte를 가지고 다시 객체로 만드는 역 직렬화의 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
public class User implements Serializable {
private final String name;
private final int age;
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
User user = new User("Dave", 30);
/* 직렬화 */
byte[] bytes = serialize(user);
/* 역 직렬화 */
User newUser = (User) deserialize(bytes);
}
/* 직렬화 메소드 */
public static byte[] serialize(Object o) throws IOException {
try (ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
try (ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos)) {
oos.writeObject(o);
return baos.toByteArray();
}
}
}
/* 역 직렬화 메소드 */
public static Object deserialize(byte[] bytes) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
try (ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes)) {
try (ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bais)) {
return ois.readObject();
}
}
}
}- 역 직렬화 :
객체 역 직렬화는ByteArrayInputStream클래스에 직렬화된 byte 값을 전달하고,ObjectInputStream클래스의readObject()메소드를 통해 객체를 얻은 후, 명시적 형 변환을 통해 올바른 객체로 변환합니다.
지금까지 자바 직렬화와 역 직렬화에 대해 알아보았습니다. 예시에는 ByteArrayOutStream을 사용하여 객체를 byte 데이터로 변환하였으나,
FileOutputStream 등을 사용하여 다양한 종류의 데이터로 변환이 가능합니다.
줄이며…
자바의 직렬화를 사용하기 위해서는 Serializable 인터페이스를 구현해야 하며, 모든 맴버변수 또한 직렬화 가능한 클래스여야 합니다.
이어서 자바 직렬화의 serialVersionUID에 대해 알아보겠습니다.